0. 概述
本文在测试中主要使用 JUnit4,结合 Mockito 和 Hamcrest,对 Controller 层的测试结合 Spring MVC Testing。所有的内容均是结合 Spring 和 JUnit4 的实践。参考程序。
1. 四阶段测试
graph LR;
Setup[Setup]
Exercise[Exercise]
Verify[Verify]
Teardown[Teardown]
Setup-->Exercise;
Exercise-->Verify;
Verify-->Teardown;
- Setup 设置:设置环境和依赖。
- Exercise 执行:执行要测试的元素。
- Verify 验证:验证预期。
- Teardown 拆卸:回收资源、删除测试数据。
一个典型的四阶段测试:
public class TypicalTest extends TestCase {
private List<Integer> list2Verify = new ArrayList<>();
// setup
public void setUp() {
list2Verify.add(1);
}
public void testExercise() {
// exercise
int i = list2Verify.get(0);
// verify
assertEquals(i, 1);
}
// teardown
public void tearDown() {
list2Verify = null;
}
}
2. 测试框架
2.1 JUnit4
注意事项
- 测试类以
Test结尾; - 方法要有
@Test注解,方法必须是public,并以test开头,返回值为void; - 推荐用
断言去验证结果,而不是简单输出结果。
上述命名规则在 JUnit4 中并非强制要求,但是如果不这样命名在使用 SonarQube 等代码质量检测软件时会得不到单元测试覆盖率。
对应四阶段测试可用的工具
Setup
@Before:在每个测试方法执行之前都会执行一次的方法。@BeforeClass:在所有测试方法执行之前只会执行一次的方法,方法必须是static的。
public class TestFixturesExample {
private ManagedResource myManagedResource;
private static ExpensiveManagedResource myExpensiveManagedResource;
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpClass() {
System.out.println("@BeforeClass setUpClass");
myExpensiveManagedResource = new ExpensiveManagedResource();
}
@Before
public void setUp() {
this.println("@Before setUp");
this.myManagedResource = new ManagedResource();
}
// test methods...
}
Exercise
@Test:每个测试类必须有的注解。@Ignore:忽略测试方法。
Verify
org.junit.Assert.*:静态断言方法。
public class AssertTests {
@Test
public void testAssertEquals() {
assertEquals("failure - strings are not equal", "text", "text");
}
@Test
public void testAssertFalse() {
assertFalse("failure - should be false", false);
}
@Test
public void testAssertNotNull() {
assertNotNull("should not be null", new Object());
}
@Test
public void testAssertNotSame() {
assertNotSame("should not be same Object", new Object(), new Object());
}
// more...
}
- @Test(excepted=Exception.class):异常测试。
@Test(expected = IndexOutOfBoundsException.class)
public void empty() {
new ArrayList<Object>().get(0);
}
Teardown
@After:在每个测试方法之后都会执行一次的方法。@AfterClass:在所有测试方法执行之后只会执行一次的方法,方法必须是static的。
public class TestFixturesExample {
private ManagedResource myManagedResource;
private static ExpensiveManagedResource myExpensiveManagedResource;
// test methods...
@After
public void tearDown() throws IOException {
this.println("@After tearDown");
this.myManagedResource.close();
this.myManagedResource = null;
}
@AfterClass
public static void tearDownClass() throws IOException {
System.out.println("@AfterClass tearDownClass");
myExpensiveManagedResource.close();
myExpensiveManagedResource = null;
}
}
2.2 Mockito
Mokito 是一个 Mock 框架,可以和 JUnit4 结合使用。
什么是 mock
Mock的意思是模拟,在软件测试中就是通过某种手段模拟被测试对象的行为,根据测试场景返回预先设计的结果。
为什么要 mock
Mock 可以解除测试对象对外部服务的依赖(如数据库,第三方接口等),使测试用例可以独立运行。
public class MockTest {
@Mock
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testSelect() {
UserEntity entity = new UserEntity();
entity.setId(1);
entity.setName("abc");
// Mock 的 userMapper 查询 id 为1的 UserEntity 时,返回预设的对象,解除了对数据库依赖
when(userMapper.selectEntity(1)).thenReturn(entity);
UserEntity entity1 = userMapper.selectEntity(1);
// other operations...
}
}
使用方法
模拟(Mock)对象
org.mockito.Mockito.mock:创建 mock 对象。
List mockedList = Mockito.mock(List.class);
@Mock:属性注解,创建 mock 对象。
public class ArticleManagerTest {
@Mock
private ArticleCalculator calculator;
}
@InjectMocks
public class ArticleManager {
ArticleManager(ArticleCalculator calculator, ArticleDatabase database) {
// parameterized constructor
}
}
public class ArticleManagerTest {
@Mock
private ArticleCalculator calculator;
@Mock(name = "database")
private ArticleDatabase dbMock;
@InjectMocks // 注入 mock 对象
private ArticleManager manager;
@Test public void shouldDoSomething() {
manager.initiateArticle();
// other operations...
}
}
设计预期
org.mockito.Mockito.when:设置 mock 对象要执行的方法。org.mockito.stubbing.BaseStubbing.*:返回预期值(thenReturn)、返回异常(thenThrow)、调用真实方法(thenCallRealMethod)等。org.mockito.stubbing.*:返回预期值(doReturn)、返回异常(doThrow)、调用真实方法(doCallRealMethod)等。public class MockTest { @Test public void testThenReturn() { List list = mock(List.class); when(list.get(0)).thenReturn("test string"); assertEquals(list.get(0), "test string"); } @Test(expected = ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.class) public void testThenThrow() { List list = mock(List.class); // 原本应该抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException when(list.get(0)).thenThrow(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.class); list.get(0); } @Test public void testCallRealMethod() { UserEntity entity = mock(UserEntity.class); when(entity.getName()).thenCallRealMethod(); entity.getName(); } }
执行验证
验证测试结果时,可以结合 Hamcrest 和 JUnit4 。
org.mockito.Mockito.verify:检验特定行为。org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.*:参数匹配器。- 验证方法调用次数:
org.mockito.Mockito.times等。
@Test
public void testVerify() {
List list = mock(List.class);
list.add("String");
list.get(0);
list.get(0);
list.get(0);
verify(list).add(anyString()); // 检验 list 放入了一个 String 类型元素
verify(list, times(3)).get(anyInt()); // 检验 list 获取了3次元素
}
2.3 Hamcrest
Hamcrest是一个用于编写匹配器对象的框架,可以与 JUnit4 集成。
public class HamcrestTest {
private List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(3);
private Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
String[] strArray = {"1", "2"};
@Before
public void setUp() {
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
map.put("1", 1);
map.put("2", 2);
map.put("3", 3);
}
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
assertThat(1, is(1));
assertThat(1, equalTo(1));
assertThat(new Object(), instanceOf(Object.class));
assertThat(null, nullValue());
assertThat(new Object(), notNullValue());
assertThat(map, Matchers.hasEntry("1", 1));
assertThat(map, Matchers.hasKey("2"));
assertThat(map, Matchers.hasValue(3));
assertThat(list, Matchers.hasItem(1));
assertThat(list, Matchers.hasItems(1, 2));
assertThat(strArray, hasItemInArray("1"));
assertThat("JY", containsString("J"));
assertThat("JY", startsWith("J"));
assertThat("JY", endsWith("Y"));
assertThat("JY", allOf(startsWith("J"), endsWith("Y")));
assertThat("JY", anyOf(startsWith("J"), endsWith("Y")));
}
}
2.4 Spring MVC Testing
Spring MVC Testing 使用流畅的 API 测试 Spring MVC 代码,可以与 JUnit4 结合使用,使用非常简单。
org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc:测试的入口。org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*:提供 HTTP 请求方法、参数等。org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.*:对测试执行结果的处理。org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.*:测试结果匹配。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Transactional
public class ControllerTest {
@Resource
private WebApplicationContext wac;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
private static ObjectMapper mapper;
@BeforeClass
public static void init() {
mapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
@Before
public void setup() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(this.wac).build();
}
/**
* get 方法.
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelect() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/user/select")
.param("id", "1")) // request 参数
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(content().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE))
.andExpect(status().is(200));
}
/**
* post 方法.
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testInsert() throws Exception {
UserDTO dto = new UserDTO();
dto.setName("fff");
mockMvc.perform(post("/user/insert")
.content(mapper.writeValueAsBytes(dto))
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
/**
* patch 方法.
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
UserDTO dto = new UserDTO();
dto.setId(1);
dto.setName("bbb");
mockMvc.perform(patch("/user/update")
.content(mapper.writeValueAsBytes(dto)) // body
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)) // content-type
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
/**
* 异常.
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void test404() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/user/notfound"))
.andExpect(status().is(404));
}
}
3. 实践
3.1 Controller 层测试
参照 2.4 Spring MVC Testing。
3.2 DAO 层测试
参照 2.2 Mockito。
3.3 数据库有关测试
最终有很多单元测试(或者集成测试)无法避免使用数据库,为了减少配置,避免不同开发者之间互相干扰,必须要控制对数据库的使用。
3.3.1 回滚数据
@Transactional:保证测试类的数据库操作可以回滚,这种最简单。- 使用
@BeforeClass、@AfterClass等方法,在测试前插入数据,测试完成后删除数据,保证测试前后数据库状态一致。
3.3.2 使用内存数据库
使用内存数据库可以保证每个开发者互不干扰,提高工作效率。以下选用的是 H2 数据库。
- 引入测试使用的内存数据库:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
- 编写数据库相关测试父类:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) // 内存数据库端口
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase(connection = EmbeddedDatabaseConnection.H2) // 内存数据库使用 H2
public class InMemoryDBTest {
// 测试方法
}
- 代码结构:表结构统一放入
schema.sql,数据放入data.sql,测试启动时内存数据库会自动加载文件内容。project -src -main -test -java -resources -application-test.properties -data.sql -schema.sql -pom.xml
在统一测试之前把所有要用的数据放入 data.sql 。测试开始时,内存数据库随之建立,数据会全部加载到内存;测试结束时,内存数据库也随之销毁,杜绝了开发者测试数据之间的相互干扰。
3.4 Spring结合其他Runner
3.4.1 Runner
测试类中没有 main 函数,Runner 是 JUnit4 中负责调用测试代码的工具,在每个测试类上加注解 @RunWith 表明当前测试类使用的 Runner。JUnit4 默认 Runner 是 BlockJUnit4ClassRunner。
它有一个限制:每个测试类只能使用一个@RunWith。
3.4.2 Spring JUnit 4 Rules
在 Spring 项目测试通常会使用 SpringRunner 或 SpringJUnit4ClassRunner,这时其他 Runner 就不能使用了。为了解决这个问题,可以在测试类里使用 SpringClassRule 和 SpringMethodRule。
SpringClassRule:支持Spring TestContext中所有类级别的特性;SpringMethodRule:支持Spring TestContext中所有实例级别的特性。
public class SpringParameterizedTest {
@ClassRule
public static final SpringClassRule SPRING_CLASS_RULE = new SpringClassRule();
@Rule
public final SpringMethodRule springMethodRule = new SpringMethodRule();
}
这时候就可以使用其他 Runner 了。
3.5 测试多种输入组合
在项目中有时会遇到一个用例要覆盖多个输入参数的各种组合,这时可以用到 JUnit4 的 Parameterized。结合 Spring 时,可使用上节介绍的内容。
// 声明使用的 Runner 是 Parameterized
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class ParameterizedTest {
@Parameterized.Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
// 定义多种输入组合
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][]{
{0, 0}, {1, 1}
});
}
private int input;
private int expected;
// 提供一个构造器
public ParameterizedTest(int input, int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(expected, input);
}
}
junit-dataprovider 对 JUnit4 进行了扩展,提供了多种输入格式。
4. 单元测试效果
本地查看
IDEA 可以查看测试覆盖率:
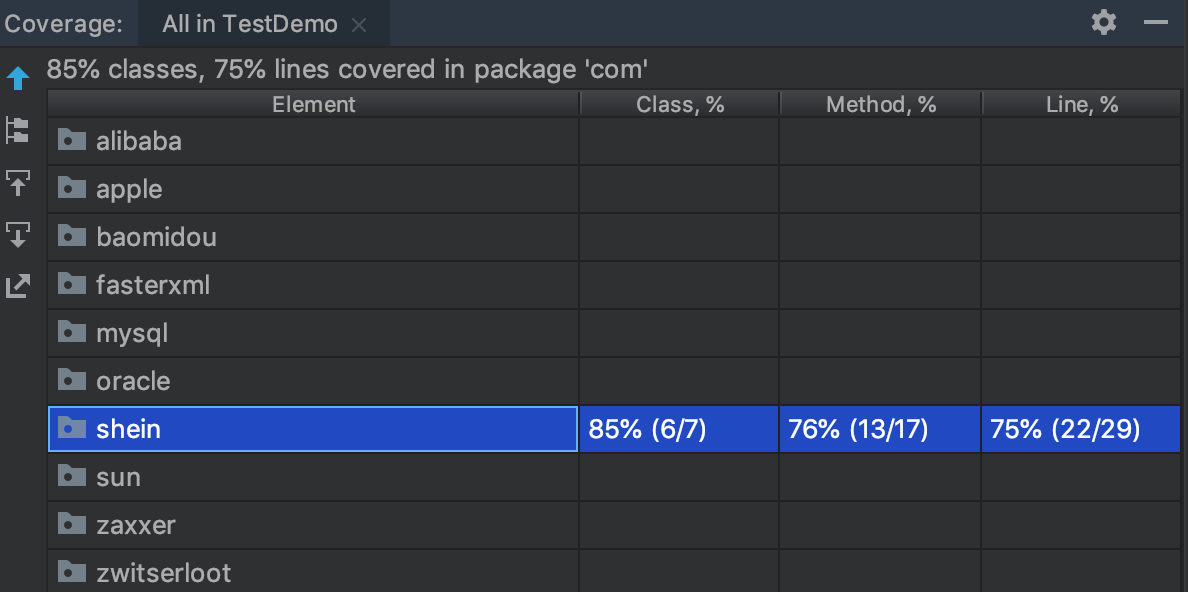
SonarQube
SonarQube 是代码质量检查的专业工具,可以单独部署或者作为 Jenkins 的插件安装。本文对此不做讨论。
5. 参考
Don’t use In-Memory Databases (H2, Fongo) for Tests