一、容器启动
容器启动后,首先会加载 Configuration Metadata,解析后编组为相应的 BeanDefinition,最后将 BeanDefinition 注册到相应的BeanDefinitionRegistry。
二、Bean 的实例化
在启动阶段,所有 bean 的信息都已经以 BeanDefinition 的方式注册到 BeanDefinitionRegistry,当方法明确地以 getBean 方法请求某个对象,或者因为对象的依赖关系隐式地请求某个对象,就会触发 Bean 的实例化。
容器会首先检查对象是否已经实例化,如果没有就会根据 BeanDefinition 的信息实例化对象,并注入依赖。如果对象实现了回调接口,也会根据回调接口的要求装配它。
三、干预 BeanFactory 的启动
Spring 提供了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的容器扩展机制。该机制允许我们在容器实例化对象之前,对注册到容器的 BeanDefinition 信息做修改。
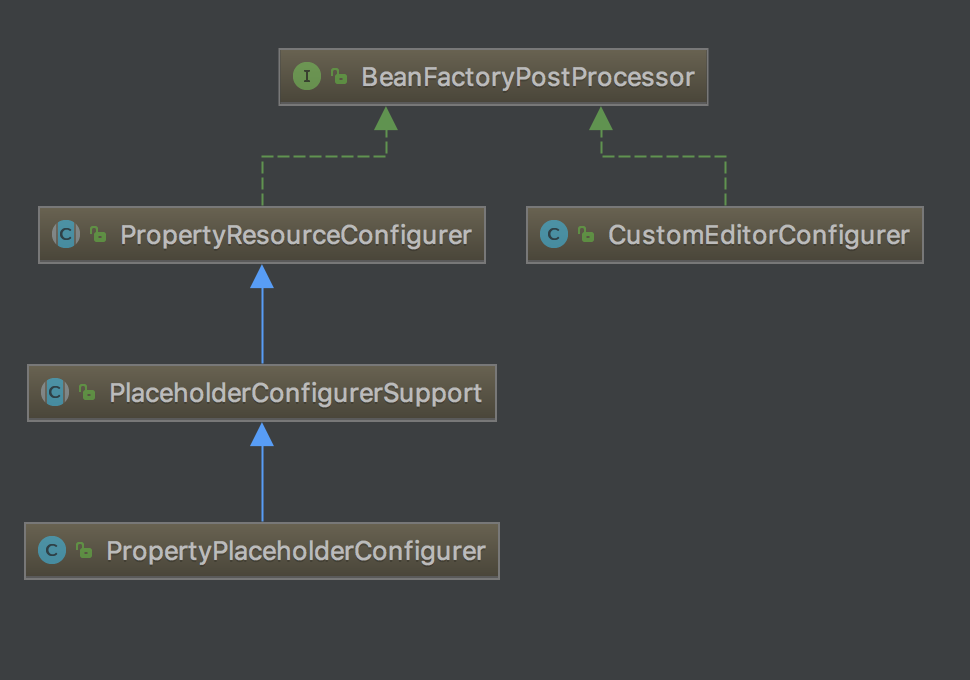
常用的实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的类:
- BeanFactory 手动应用所有 BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("..."));
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer propertyPostProcessor = new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(); propertyPostProcessor.setLocation(new ClassPathResource("..."));
propertyPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- ApplicationContext ApplicationContext 会自动识别 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 并装配:
<beans>
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>conf/jdbc.properties</value>
<value>conf/mail.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>